
by Johnson and Dugan | Aug 2, 2017 | Benefit Management

Tired of celebrating the 10% increase? Join us in an innovative discussion on reducing your Health Insurance Premium through Creative Financing for your benefit program. Learn about turning a 10% increase into a 25% decrease.
Keynote Speaker:
Clifford Der, East West Administrators
We will be discussing alternative funding from traditional Self-Funding to Medical Expense Reimbursement Plans. We will also address any legal questions you may have regarding your liability as an employer offering a fully insured program versus a self-funded program.
11:45 a.m. – 12:00 p.m. Registration
12:00 p.m. – 1:00 p.m. Seminar & Complimentary Buffet Lunch
Location: Mistral Restaurant and Bar | 370-6 Bridge Parkway | Redwood Shores, CA 94065
Click Here To Register
About the Presenter:
Clifford Der, East West Administrators – Clifford has been a member of the National Association of Health Underwriters for more than 40 years. His extensive background in healthcare benefits includes developing the Chinese Community Health Plan (EPO-a first in the country), the first acupuncture plan, the development of the Medical Expenses Reimbursement Plans along with custom designed Partial Self-funded Health Plans.
Sponsored by:




by admin | Jul 31, 2017 | COBRA, Human Resources
 The Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1985 (COBRA) requires group health plans to provide notices to covered employees and their families explaining their COBRA rights when certain events occur. The initial notice, also referred to as the general notice, communicates general COBRA rights and obligations to each covered employee (and his or her spouse) who becomes covered under the group health plan. This notice is issued by the plan administrator within the first 90 days when coverage begins under the group health plan and informs the covered employee (and his or her spouse) of the responsibility to notify the employer within 60 days if certain qualifying events occur in the future.
The Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1985 (COBRA) requires group health plans to provide notices to covered employees and their families explaining their COBRA rights when certain events occur. The initial notice, also referred to as the general notice, communicates general COBRA rights and obligations to each covered employee (and his or her spouse) who becomes covered under the group health plan. This notice is issued by the plan administrator within the first 90 days when coverage begins under the group health plan and informs the covered employee (and his or her spouse) of the responsibility to notify the employer within 60 days if certain qualifying events occur in the future.
The initial notice must include the following information:
- The plan administrator’s contact information
- A general description of the continuation coverage under the plan
- An explanation of the covered employee’s notice obligations, including notice of
- The qualifying events of divorce, legal separation, or a dependent’s ceasing to be a dependent
- The occurrence of a second qualifying event
- A qualified beneficiary’s disability (or cessation of disability) for purposes of the disability extension)
- How to notify the plan administrator about a qualifying event
- A statement that the notice does not fully describe continuation coverage or other rights under the plan, and that more complete information regarding such rights is available from the plan administrator and in the plan’s summary plan description (SPD)
As a best practice, the initial notice should also:
- Direct qualified beneficiaries to the plan’s most recent SPD for current information regarding the plan administrator’s contact information.
- For plans that include health flexible spending arrangements (FSAs), disclose the limited nature of the health FSA’s COBRA obligations (because certain health FSAs are only obligated to offer COBRA through the end of the year to qualified beneficiaries who have underspent accounts).
- Explain that the spouse may notify the plan administrator within 60 days after the entry of divorce or legal separation (even if an employee reduced or eliminated the spouse’s coverage in anticipation of the divorce or legal separation) to elect up to 36 months of COBRA coverage from the date of the divorce or legal separation.
- Define qualified beneficiary to include a child born to or placed for adoption with the covered employee during a period of COBRA continuation coverage.
- Describe that a covered child enrolled in the plan pursuant to a qualified medical child support order during the employee’s employment is entitled to the same COBRA rights as if the child were the employee’s dependent child.
- Clarify the consequences of failing to submit a timely qualifying event notice, timely second qualifying event notice, or timely disability determination notice.
Practically speaking, the initial notice requirement can be satisfied by including the general notice in the group health plan’s SPD and then issuing the SPD to the employee and his or her spouse within 90 days of their group health plan coverage start date.
If the plan doesn’t rely on the SPD for furnishing the initial COBRA notice, then the plan administrator would follow the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) rules for delivery of ERISA-required items. A single notice addressed to the covered employee and his or her spouse is allowed if the spouse lives at the same address as the covered employee and coverage for both the covered employee and spouse started at the time that notice was provided. The plan administrator is not required to provide an initial notice for dependents.
By Danielle Capilla
Originally Posted By www.ubabenefits.com
by admin | Jul 25, 2017 | Group Benefit Plans, Health Plan Benchmarking
 Modern medicines have resulted in longer, more productive lives for many of us. Prescription drugs soothe sore muscles after a strenuous workout or manage the conditions of a chronic disease. Unfortunately, this use of prescriptions drugs can come with a hefty price tag.
Modern medicines have resulted in longer, more productive lives for many of us. Prescription drugs soothe sore muscles after a strenuous workout or manage the conditions of a chronic disease. Unfortunately, this use of prescriptions drugs can come with a hefty price tag.
Americans are spending more money on prescription drugs than ever before and the United States as a nation spends more per capita on prescription drugs than any other country. With the cost of some drugs exceeding thousands of dollars for a 30-day supply, this can translate into financial hardship for many Americans.
For employers sponsoring a medical plan, managing the cost of these prescription drugs is also becoming a task. Insurance companies and employers struggle with the ability to provide affordable medical plans, and the ever-increasing prescription drug costs are a primary driver of this difficulty. As a result, prescription drug plan designs are changing shape – moving to a model that helps push more of the cost of these drugs to the member along with increasing awareness of the true cost of the prescriptions.
Flat dollar copay plans have become an expected norm in medical plans for almost a decade. However, insurance companies underwriting fully insured medical plans and employers sponsoring self-funded medical programs now need to make modifications to these plan designs to manage the ever-increasing prescription drug costs. As a result, we are seeing more prescription drug plans combining some aspect of coinsurance along with or in place of the flat dollar copayments.
According to the 2016 UBA Health Plan Survey, copay models are still the most popular, with a three-tier copay structure the most prevalent. Median retail copayments for these three-tier plans are $10 for generic drugs, $35 for preferred brand drugs (drugs on the carrier’s prescription drug list) and $60 for non-preferred brand drugs (drugs not on the carrier’s prescriptions drug list). While 54.5 percent of all prescription plans are copay only, approximately 40 percent of all prescription drug plans have co-insurance along with (or in lieu of) copays–a plan design that is particularly common among four-tier plans.
Coinsurance models have many unique designs. Some plans are a straight percentage of the cost of the drug; some may involve a maximum or minimum dollar copayment combined with the coinsurance. For example, a plan may require 40 percent coinsurance for a preferred brand drug, but there is a minimum copayment of $30 and a maximum copayment of $50. Typically, we see a higher coinsurance percentage for non-preferred brand drugs and specialty drugs. The member cost of the drug is calculated after any negotiated discounts, so members covered by a coinsurance plan are reaping the benefits of any discounts negotiated with the pharmacy by the pharmacy benefit manager (PBM).
Coinsurance plans do provide several advantages to managing prescription drug costs. Under a flat dollar copay plan design, members may not truly understand the full cost of the drug they are purchasing. Pharmacies are now disclosing the full cost of drugs on the purchase receipts. Yet, most consumers do not take note of this disclosure, focusing only on the copayment amount. When a member pays a percentage of the cost of the drug as in a coinsurance model, the true cost of the drug becomes much more apparent.
Another advantage of the coinsurance model is that it automatically increases the member share of the cost as the price of the drug increases. Under the flat dollar copayment model, as the true cost of the drug increases, the member pays a smaller portion of the total cost. When the member’s portion is determined by a coinsurance percentage, the member pays more as the cost of the drug increases.
As the costs of health care overall continue to increase, we all need to become better consumers of our healthcare. Members covered by a prescription drug plan with a coinsurance model will have a better understanding of the true cost of their prescriptions. As members become more aware of the true costs of their care, they make better health care decisions, managing the overall cost of care.
We expect to see prescription drug benefit plans change even more as the cost of health care – especially prescription drugs – escalates. These changes will likely result in more of the cost being pushed to the patient. There are resources available to patients for assistance with some of these out-of-pocket costs. It is vital for the patient to understand their costs and know how to maximize their benefits. In a few weeks, the UBA blog will highlight some of these resources and provide information on how to educate employees on maximizing their benefits and the industry resources available to them.
For all the cost and design trends related to health and prescription drug plan costs by group size, industry and region, download UBA’s Health Plan Survey Executive Summary.
By Mary Drueke-Collins
Originally Posted By www.ubabenefits.com

by admin | Jun 16, 2017 | HSA/HRA
 The average employer contribution to an HSA is $474 for a single employee (down 3.5 percent from 2015 and 17.6 percent from five years ago) and $801 for a family (down 9.2 percent from last year and 13.7 percent from five years ago). There was a 26 percent increase in the number of individuals enrolled in HSAs, likely due to the increase in CDHP enrollment (which often have HSAs tied to them). Since 2013, there has been a 97.7 percent increase in enrollment, showing significant employer and employee interest in these plans over time.
The average employer contribution to an HSA is $474 for a single employee (down 3.5 percent from 2015 and 17.6 percent from five years ago) and $801 for a family (down 9.2 percent from last year and 13.7 percent from five years ago). There was a 26 percent increase in the number of individuals enrolled in HSAs, likely due to the increase in CDHP enrollment (which often have HSAs tied to them). Since 2013, there has been a 97.7 percent increase in enrollment, showing significant employer and employee interest in these plans over time.
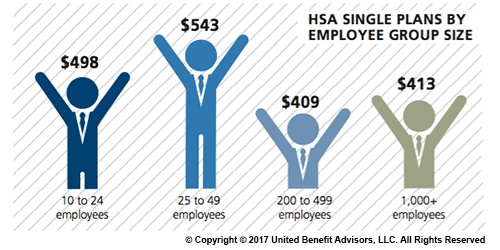
Looking at contributions by group size, singles at companies with 200 to 499 employees receive the lowest HSA contributions ($409). Singles at some of the smallest companies (25 to 49 employees) receive the most generous contributions ($543), on average.
Like their single counterparts, families get more generous contributions from small employers. The average family HSA contribution in groups with 25 to 49 employees was $908 (though, in general, small employer contributions have been declining over time).
Last year, some of the smallest companies (10 to 24 employees) had the highest HSA enrollment (16.3 percent). However, rapid enrollment increases among large employers in recent years now places the largest companies (1,000+ employees) as HSA enrollment leaders with 19.1 percent enrolled.
For a detailed look at the prevalence and enrollment rates among HSA and HRA plans by industry and region, view UBA’s “Special Report: How Health Savings Accounts Measure Up”, to understand which aspects of these accounts are most successful, and least successful.
Benchmarking your health plan with peers of a similar size, industry and/or geography makes a big difference in determining if your plan is competitive. To compare your exact plan with your peers, request a custom benchmarking report.
For fast facts about HSA and HRA plans, including the best and worst plans, average contributions made by employers, and industry trends, download (no form!) “Fast Facts: HSAs vs. HRAs”.
By Bill Olson
Originally Posted By www.ubabenefits.com
by admin | Jun 9, 2017 | HSA/HRA, IRS
IRS Releases 2018 Amounts for HSAs
The IRS released Revenue Procedure 2017-37 that sets the dollar limits for health savings accounts (HSAs) and high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) for 2018.
For calendar year 2018, the annual contribution limit for an individual with self-only coverage under an HDHP is $3,450, and the annual contribution limit for an individual with family coverage under an HDHP is $6,900. How much should an employer contribute to an HSA? Read our latest news release for information on modest contribution strategies that are still driving enrollment in HSA and HRA plans.
For calendar year 2018, a “high deductible health plan” is defined as a health plan with an annual deductible that is not less than $1,350 for self-only coverage or $2,700 for family coverage, and the annual out-of-pocket expenses (deductibles, co-payments, and other amounts, but not premiums) do not exceed $6,650 for self-only coverage or $13,300 for family coverage.
Retroactive Medicare Coverage Effect on HSA Contributions
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) recently released a letter regarding retroactive Medicare coverage and health savings account (HSA) contributions.
As background, Medicare Part A coverage begins the month an individual turns age 65, provided the individual files an application for Medicare Part A (or for Social Security or Railroad Retirement Board benefits) within six months of the month in which the individual turns age 65. If the individual files an application more than six months after turning age 65, Medicare Part A coverage will be retroactive for six months.
Individuals who delayed applying for Medicare and were later covered by Medicare retroactively to the month they turned 65 (or six months, if later) cannot make contributions to the HSA for the period of retroactive coverage. There are no exceptions to this rule.
However, if they contributed to an HSA during the months that were retroactively covered by Medicare and, as a result, had contributions in excess of the annual limitation, they may withdraw the excess contributions (and any net income attributable to the excess contribution) from the HSA.
They can make the withdrawal without penalty if they do so by the due date for the return (with extensions). Further, an individual generally may withdraw amounts from an HSA after reaching Medicare eligibility age without penalty. (However, the individual must include both types of withdrawals in income for federal tax purposes to the extent the amounts were previously excluded from taxable income.)
If an excess contribution is not withdrawn by the due date of the federal tax return for the taxable year, it is subject to an excise tax under the Internal Revenue Code. This tax is intended to recapture the benefits of any tax-free earning on the excess contribution.
By Danielle Capilla
Originally Posted By www.ubabenefits.com



![]()





